Microsoft Speech to Text¶
Overview¶
The Microsoft Speech-to-Text Service in AIForged uses Microsoft’s Azure AI Speech to accurately transcribe audio into text across many languages. Transcripts are stored in the document’s Result property for downstream search, analytics, or workflow automation. Models can be tailored to improve accuracy for domain-specific vocabulary.
Info
Tip: Use this service to quickly turn recorded meetings, calls, or podcasts into searchable, actionable text. For structured data extraction from documents, use Document Intelligence.
Permissions Required¶
Members must belong to one of the following AIForged user group roles to add and configure this service:
- Owner
- Administrator
- Developer
Info
Tip: Role membership is managed in Organisations > Roles. Assign members to roles to grant agent and service administration access.
Supported Content Types¶
- MP3
- WAV (PCM)
Info
Tip: If your audio is in another format (e.g., M4A, AAC, OGG), transcode it to MP3 or WAV using your preferred media converter before uploading.
Possible Use Cases¶
- Generate meeting minutes or summaries from recorded sessions.
- Transcribe customer calls for QA, analytics, or compliance.
- Produce captions/subtitles for training videos and webinars.
- Extract music lyrics or spoken content from audio tracks (subject to licensing).
Service Setup¶
Follow these steps to add and configure the Microsoft Speech-to-Text Service to your agent:
- Open the Agent View: Navigate to the agent where you want to add the service.
- Add the Microsoft Speech-to-Text Service:
Click the Add Service
 button.
button. - Select Service Type:
Choose Microsoft Speech-to-Text Service from the available service types.
- Configure the Service Wizard
- Open the Service Configuration Wizard.
- Or
-
Step 1: General Settings: Configure the service name, description, and core settings. Default settings are sufficient for most use cases.
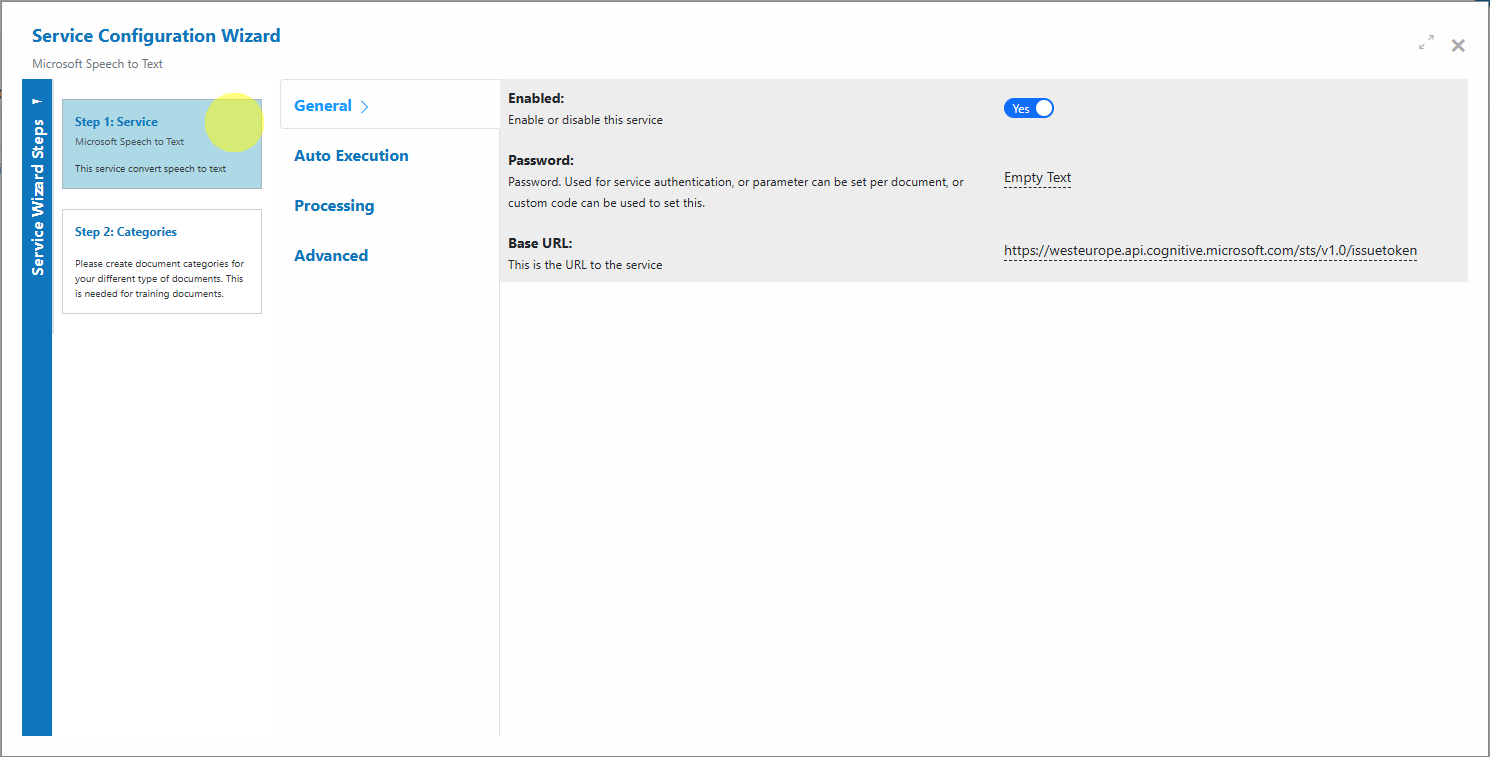
Service Configuration Settings¶
Most users can proceed with the default settings. Advanced configuration is available for custom workflows.
| Setting | Type | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArchivingStrategy | Optional | No | Number of days before documents are deleted. |
| AccessKey | Optional | No | Override the Microsoft cloud access key (typically not required in AIForged). |
| BaseURL | Optional | No | Override the Speech-to-Text endpoint (advanced; usually not required). |
| BatchSize | Hidden | - | Processing batch size. |
| DocumentProcessedStatus | Optional | No | Status applied after successful transcription. |
| Enabled | Hidden | - | Enable or disable the service. |
| ExecuteBeforeProcess | Optional | No | If configured as a child service, execute before the parent service. |
| ExecuteAfterProcess | Optional | No | If configured as a child service, execute after the parent service. |
| Language | Optional | No | Specify the primary spoken language of the audio (e.g., en-US). |
| Password | Optional | No | Authentication/password handling; can be set per document via Custom Code. |
| RemoveComments | Optional | No | Remove human comments/annotations in document metadata (not typical for audio). |
Info
Tip: If unsure, keep defaults unless you have a specific processing or integration requirement. Setting the correct Language improves transcription accuracy.
Add and Process Documents¶
To upload and process audio using the Microsoft Speech-to-Text Service:
- Open Service: When you open the Microsoft Speech-to-Text Service, you will be presented with the documents currently queued or processed in the Inbox.
- Upload Audio:
Click the Upload
 button or drag and drop files over the document grid (MP3 or WAV).
button or drag and drop files over the document grid (MP3 or WAV).
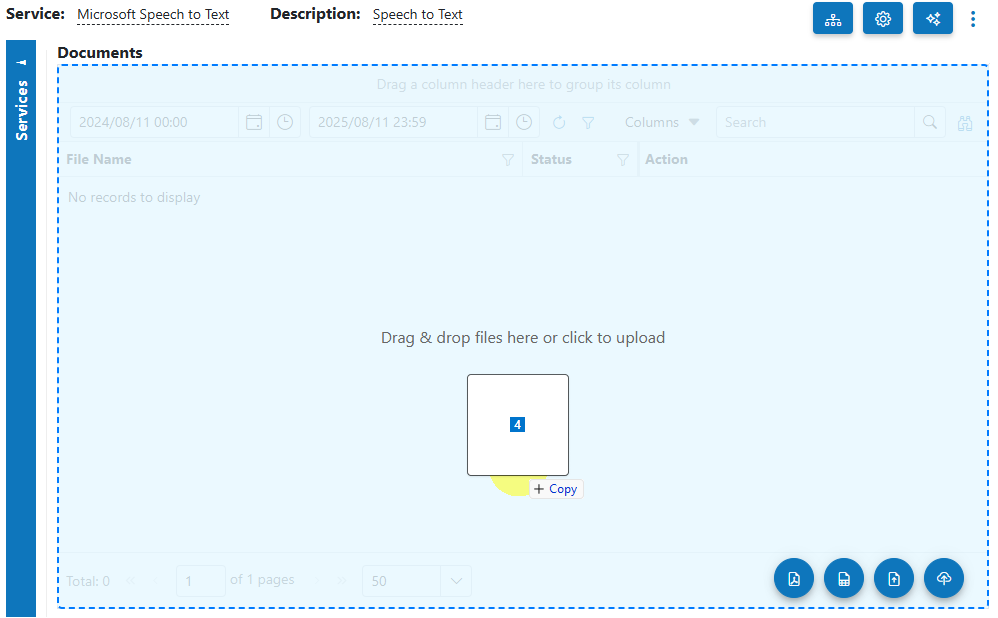
- Select Category (Optional): If you know the category for the audio, select it. Otherwise, select No category.
- Process Documents: After uploading, select the audio files to process and click Process Checked.
Info
Tip: For new services, process a small batch first to verify transcription quality before scaling up.
View Processed Documents¶
- Select Outbox in the usage filter in the Microsoft Speech-to-Text Service.
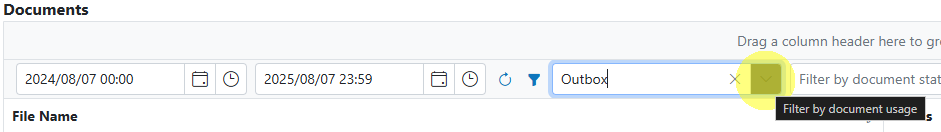
- Open any processed document to view the transcript in the Result property.
Troubleshooting Tips¶
- Transcript missing words or inaccurate?
- Ensure clear audio: minimize background noise, echo, or music.
- Set the correct Language (e.g., en-GB vs en-US).
- Prefer mono recordings with consistent levels; avoid clipping.
- Long files take a while to complete?
- Longer recordings may be processed asynchronously by the provider and take more time.
- Split very long audio into smaller segments to keep processing responsive.
- Audio won’t process?
- Confirm the file format is MP3 or WAV and not DRM‑protected/encrypted.
- Re‑export the audio with a standard codec and a constant sample rate (e.g., 16 kHz mono WAV or 128 kbps mono MP3).
- Multiple speakers in a single recording?
- Overlapping speakers and crosstalk reduce accuracy; use separate microphones when possible or pre-segment the audio.
Best Practices¶
- Record at a consistent level in a quiet environment; reduce background noise and reverberation.
- Use mono channels for speech; 16 kHz or higher sample rate is recommended for better accuracy.
- Set the correct Language to match the audio content.
- Trim long silences and split long recordings into smaller parts for faster, more reliable processing.
- Validate a representative sample before large-scale processing, and standardize your capture/export settings across sources.