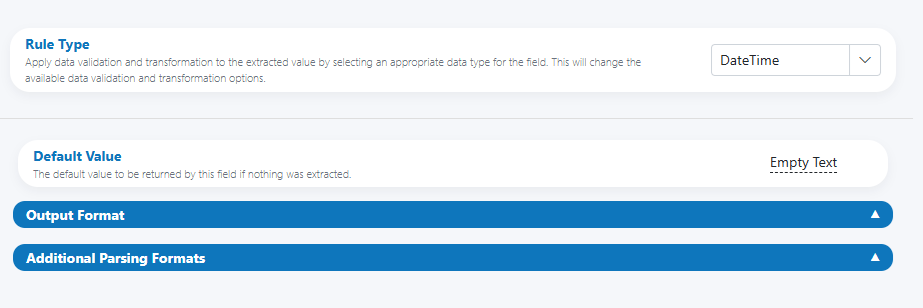
DateTime¶
Use the DateTime Rule Type when a field should contain a valid date, time, or a combined date‑time. The rule parses varied input formats (across locales), normalizes the value, and can enforce business ranges (e.g., not in the future/past).
When to use¶
- Document dates: invoice date, due date, statement date, posting date.
- Operational timestamps: delivery date/time, check‑in/out, appointment time.
- Any field that must be reliably parsed and formatted as a date/time for downstream systems.
Open Field Configuration¶
See Field Rules (Rules Engine) for how to open the field configuration:
- From the document overlay (supported services), or
- From the Fields panel on the right sidebar.
Configure the DateTime rule¶
Core settings:
- Rule Type: DateTime
- Default Value: The value to return when nothing is extracted (e.g., Empty Text or a business default)
Output Format panel:
- Culture Language Code (e.g.,
en,fr) - Culture Country Code (e.g.,
US,ZA) - Minimum value (optional)
- Maximum value (optional)
Quick start
If most inputs are in one locale, set Culture Language/Country for that locale and add only a few extra input formats under “Additional Parsing Formats” to cover the common edge cases.
Input parsing and normalization¶
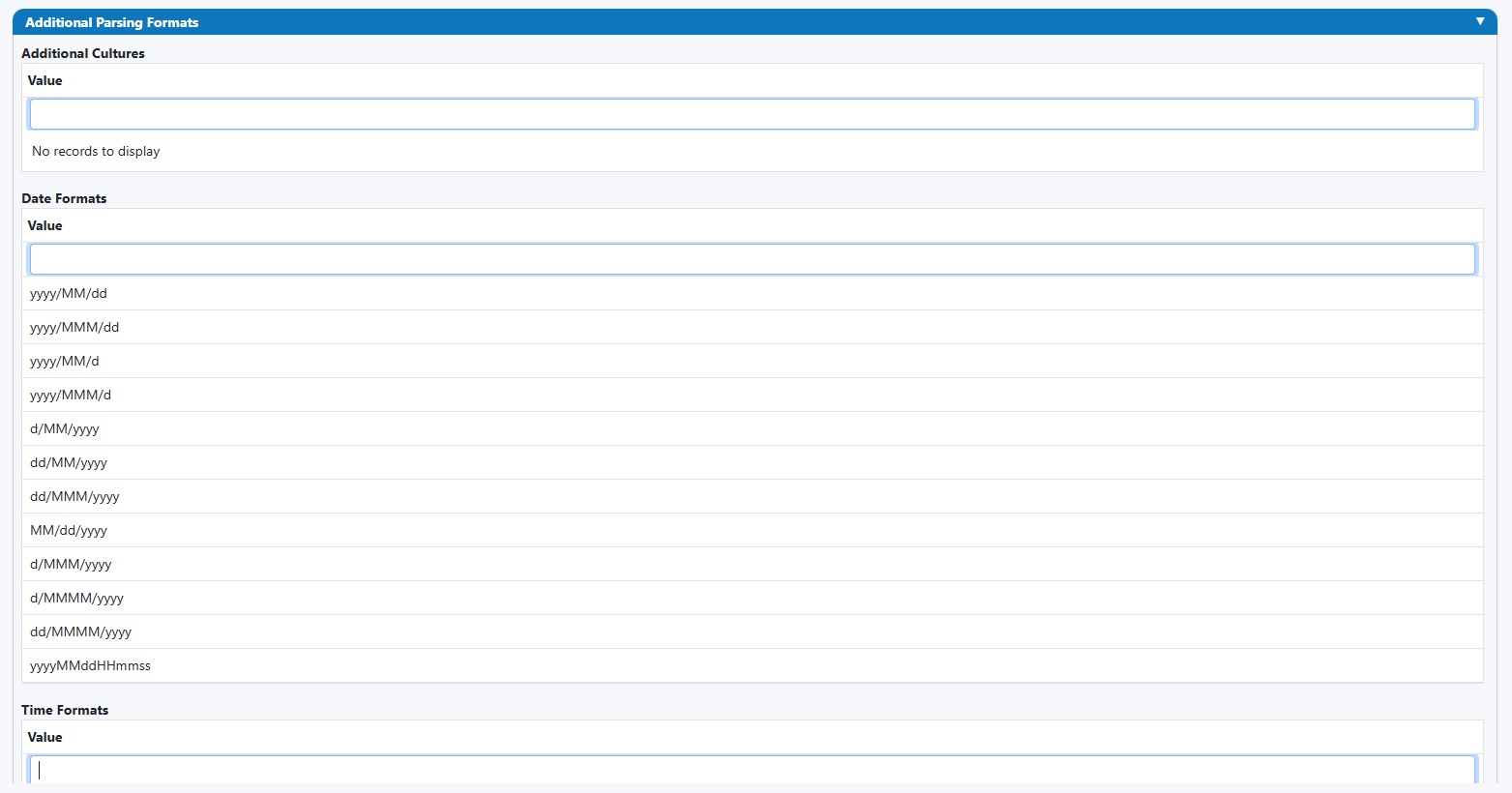
Use “Additional Parsing Formats” to accept multiple input styles while producing one consistent output.
-
Additional Cultures (optional)
- Add culture codes you want to accept during parsing (e.g.,
en-GB,de-DE), so day/month order and month names are interpreted correctly.
- Add culture codes you want to accept during parsing (e.g.,
-
Date Formats
- Provide one or more format strings to match expected date inputs. Examples:
yyyy/MM/dddd/MM/yyyyMM/dd/yyyydd/MMM/yyyy(e.g., 05/Jan/2025)dd/MMMMM/yyyy(e.g., 05/January/2025)yyyyMMddHHmmss(combined stamp)
- Provide one or more format strings to match expected date inputs. Examples:
-
Time Formats
- Provide expected time inputs. Examples:
HH:mmHH:mm:sshh:mm tt(e.g., 03:45 PM)
- Provide expected time inputs. Examples:
Order of evaluation
The engine evaluates the configured formats from top to bottom and uses the first match. Keep the most common formats near the top.
Token refresher
dd= day (01–31)MM= month (01–12),MMM= abbreviated month (Jan),MMMM= full month (January)yy/yyyy= year (two/four digits)HH= 24‑hour,hh= 12‑hour,mm= minutes,ss= seconds,tt= AM/PM
Avoid ambiguity
Mixing dd/MM/yyyy and MM/dd/yyyy can cause day/month swaps. Prefer one default (e.g., based on Culture) and add the other only if truly necessary.
Output and formatting¶
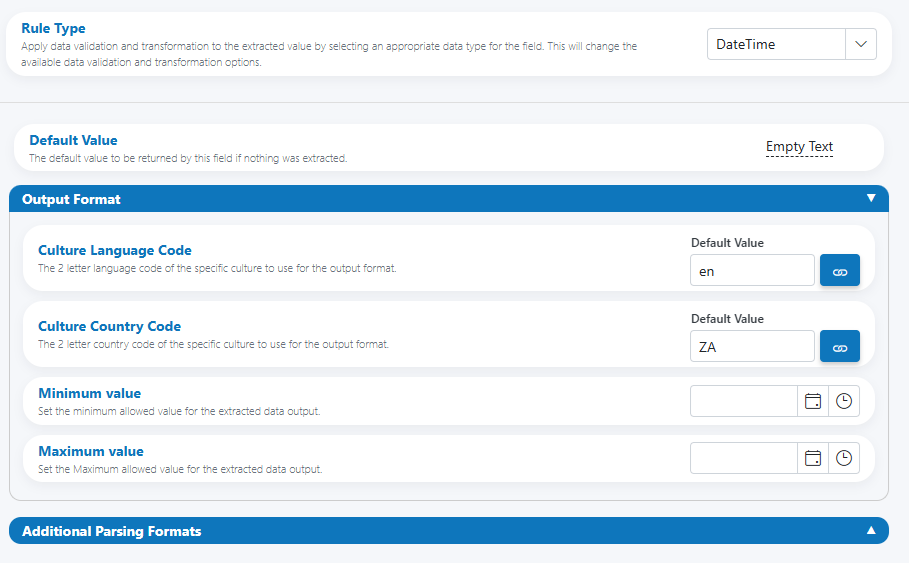
- Culture Language/Country determine the final display formatting (date order, month names, AM/PM vs 24‑hour).
- Minimum/Maximum value enforce business rules (e.g., within the last 10 years; not more than 30 days in the future).
Common output conventions:
- For US‑style output (month/day/year): set Language
en, CountryUS. - For ISO‑like reporting, consider using an ISO format downstream once parsed (e.g., by your export/reporting layer).
Range controls
Use Minimum/Maximum to catch outliers such as 1901 instead of 2021 or a due date far in the past/future due to OCR errors.
HITL triggers and reviewer guidance¶
Recommended escalation conditions:
- Parsing failed under all configured cultures and formats.
- The parsed value is outside Minimum/Maximum range.
- The input suggests an ambiguous format (e.g., 03/04/2025 where day/month can be swapped) and confidence is low.
- A 2‑digit year is used and the century rule would materially impact decisions.
Suggested reviewer note
“Confirm the date format and correct if needed. Expected formats: dd/MM/yyyy or yyyy/MM/dd; time optional (HH:mm).”
Examples¶
-
Accept EU and US inputs, format as South Africa
- Output: Language
en, CountryZA - Additional Cultures:
en-GB,en-US - Date Formats:
dd/MM/yyyy,MM/dd/yyyy,dd/MMM/yyyy - Time Formats:
HH:mm,HH:mm:ss - Min/Max: last 10 years to +30 days
- Output: Language
-
Long month names and 12‑hour time
- Output: Language
en, CountryUS - Date Formats:
d MMMM yyyy(e.g., 9 January 2025) - Time Formats:
hh:mm tt(e.g., 03:45 PM)
- Output: Language
-
Compact timestamps
- Date Formats:
yyyyMMdd - Time Formats:
HHmmss - Combined:
yyyyMMddHHmmssto capture date and time in a single token
- Date Formats:
Ambiguity guardrail
If both dd/MM/yyyy and MM/dd/yyyy are enabled, require at least one format with a month name (dd/MMM/yyyy) to disambiguate common day/month swaps for review.
Best practices¶
- Parse wide, format narrow: accept realistic variations; output one consistent culture.
- Prefer four‑digit years (
yyyy) to avoid century errors. - Include at least one format with month names (
MMM/MMMM) if numeric day/month may be ambiguous. - Use Min/Max ranges to catch outliers caused by OCR artifacts.
- Keep the format list concise—more formats can increase false positives.
Testing checklist¶
- [ ] Provide samples covering each configured Date/Time format.
- [ ] Include numeric and text month variants (e.g., 01/02/2025 and 01/Feb/2025).
- [ ] Test 24‑hour vs 12‑hour (
HH:mmvshh:mm tt). - [ ] Validate boundary cases: leap years (29/02), end of month (31/04 invalid), midnight/noon.
- [ ] Verify Min/Max range enforcement and corresponding HITL triggers.
- [ ] Confirm output rendering matches the selected Culture.
Troubleshooting¶
-
Value won’t parse
Move the likely format higher in the list; add the missing format; add the source culture to Additional Cultures. -
Day/month swapped
Reduce conflicting numeric formats; add a month‑name format; review Culture settings. -
Incorrect AM/PM or 24‑hour interpretation
Ensure the correct time format token is configured (hh:mm ttvsHH:mm). -
Out‑of‑range errors
Adjust Min/Max to reflect business rules; check OCR for truncated years or wrong century.
UI reference¶
-
Base panel (Rule Type, Default Value)

-
Output Format (culture and range)

-
Additional Parsing Formats (cultures, date/time formats)
