Script¶
Use the Script enhancement to run custom logic on a single field’s value after extraction and before downstream steps. It’s ideal for validations, transformations, enrichment, and specialized policies that go beyond built‑in Rule Types. This field-level script uses the same runtime as your Custom Code utilities and exposes the BaseModule and related modules you already know.
When to use¶
- Apply business rules to a specific field after extraction (normalize, reformat, validate).
- Cross‑check a field against other fields, datasets, or reference services.
- Perform lightweight enrichment (e.g., call an API, compute a checksum).
- Influence HITL by adding verification notes/status or adjusting confidence with policy.
Open Field Configuration¶
See Field Rules (Rules Engine) for how to open the field configuration:
- From the document overlay (supported services), or
- From the Fields panel on the right sidebar.
Configure the Script enhancement¶
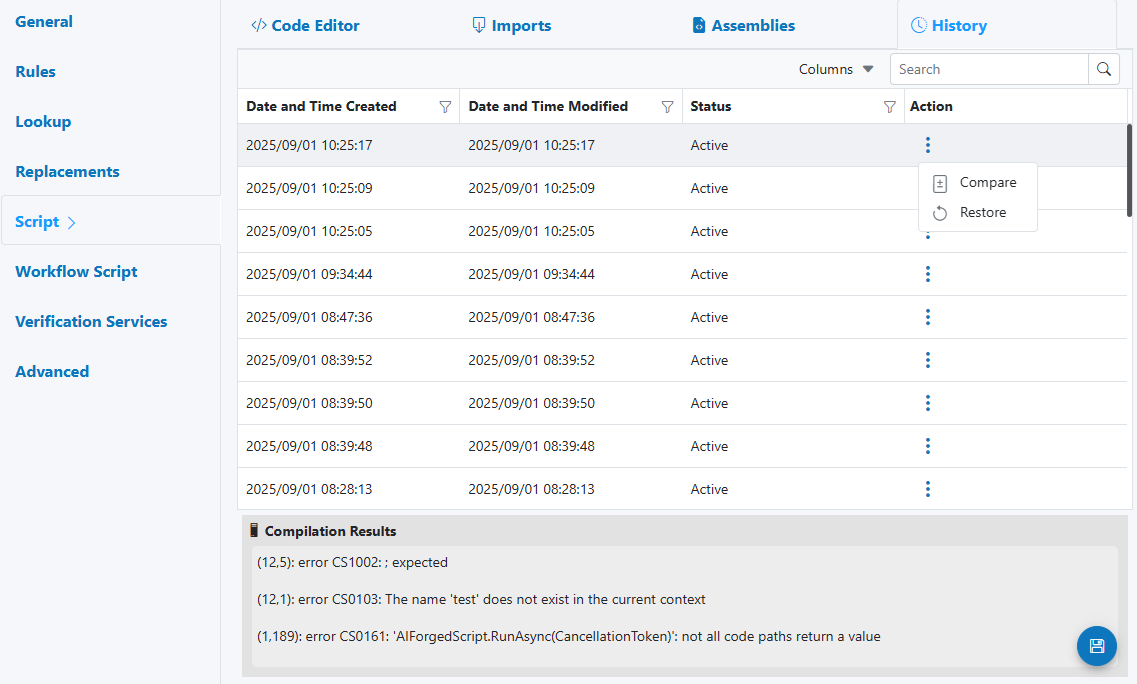
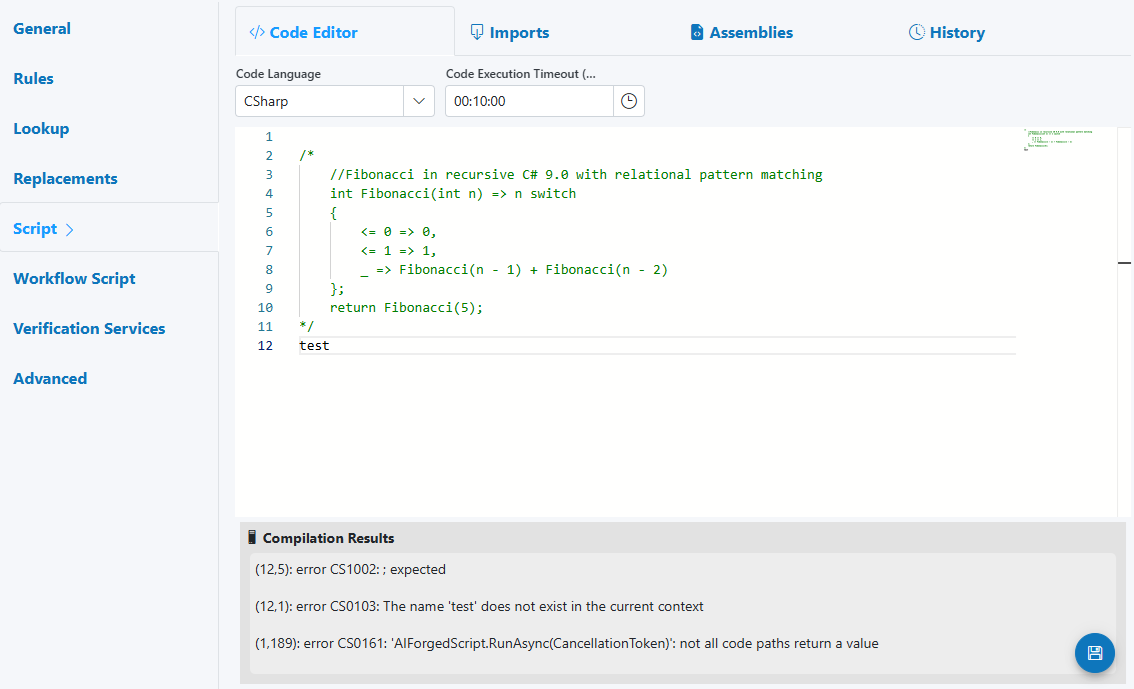
The Script panel includes four tabs:
-
Code Editor
- Code Language (C#, Visual Basic, F#, IronPython; SemanticKernel if enabled)
- Code Execution Timeout
- Editor with compile/run feedback (Compilation Results)
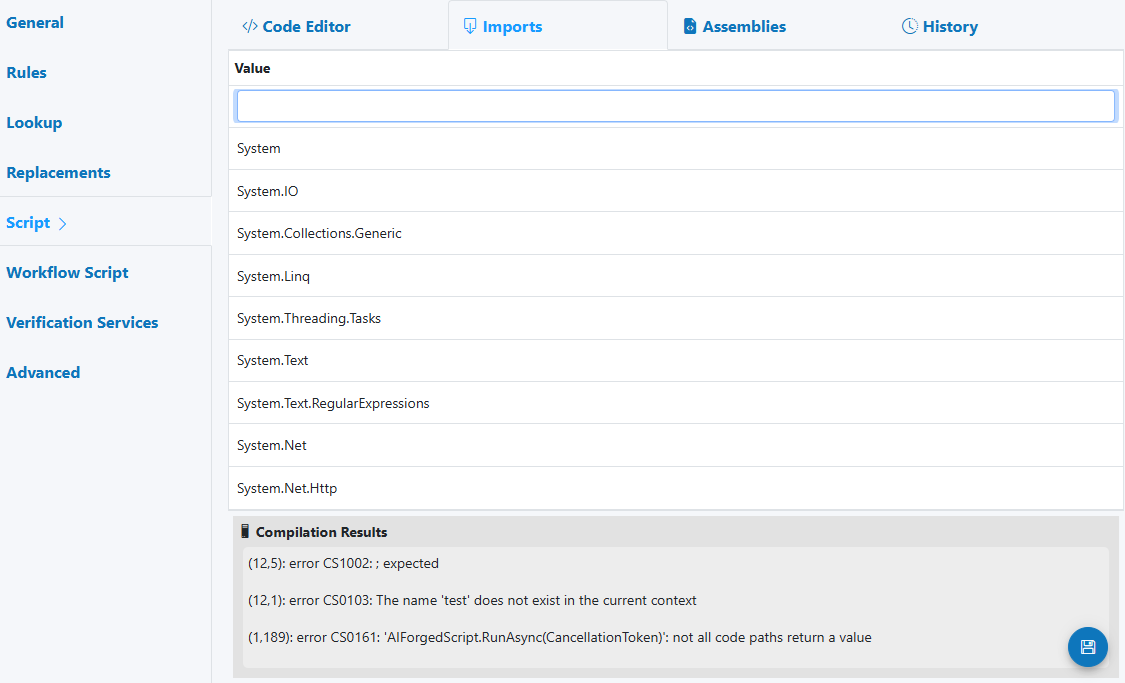
-
Imports
- Add namespaces to simplify references (e.g., System.Text.RegularExpressions)
-
Assemblies
- Reference additional .NET assemblies (e.g., System.Net.Http) required by your script
-
History
- Versioned changes, with Compare and Restore
Execution model and return contract¶
- Scope: Runs for the specific field (Parameter Definition) it is attached to.
- Order (typical Field Enhancements pipeline): Replacements → Lookup → Script → Verification Services → Workflow Script
- Input: verification (current field value, confidence, and context)
- Output: Return a ProcessResult constructed with the (possibly updated) verification
return verification;
Supported languages¶
- C#
- IronPython
- SemanticKernel (Natural language coding)
Tip
Prefer C# for best sample coverage and API access. Use IronPython if your team is Python‑centric. SemanticKernel can accelerate natural‑language logic and prototypes.
What’s available in scripts (BaseModule overview)¶
Your field script has access to the same BaseModule APIs as service‑level Custom Code. See:
- Base module and types: BaseModule / IBaseModule
- Full overview: Custom Code
Commonly used modules/capabilities:
- Parameters and Verifications
- Read/update current field value and confidence
- Add verification entries, statuses, and reviewer notes
- Documents and Services
- Access document metadata, pages, other fields (read/update as policy allows)
- Datasets
- Query your Custom Datasets (allowed lists, product catalogs, policies)
- Work Items (HITL)
- Signal or add guidance for review routing (often via verification statuses/notes)
- Webhooks and Notifications
- Trigger downstream hooks when specific conditions are met
- HTTP/Networking
- Call approved external APIs (respect timeouts/retries)
- Storage/Files
- Read/write attachments or artifacts (where permitted)
- Utilities
- JSON serialization, regex helpers, date/number parsing
Security
Only use approved endpoints/assemblies; keep secrets in secure configuration, not in code.
Reference: field‑level script context (globals)¶
These objects are available to your field‑level script at runtime:
- module: TModule (implements IBaseModule; your entry point to AIForged APIs)
- project: IProject (current project context)
- stpd: IParameterDef (the selected Parameter Definition for this field)
- stl: int (selected language ID/index context, if applicable)
- rule: BaseOption (the active rule option object, when relevant)
- logger: ILogger (logging interface)
Current document/field context:
- doc: IDocument (the current document)
- par: IDocumentParameter (the current field’s parameter instance on this document)
- def: IParameterDef (alias of stpd for convenience)
- verification: IVerification (the current field’s verification object)
- step: VerificationStep (current verification step)
IVerificationModule additions available via the field script context:
- Properties:
- Doc: IDocument
- Par: IDocumentParameter
- Def: IParameterDef
- Verification: IVerification
- Step: VerificationStep
- Methods:
- FindParameter(pdId, includeVerification = false, index = null): locate another parameter by definition ID (optionally include verification, or an index for repeating fields)
- FindParameterByParentIndex(pdId, parentName, includeVerification = false): locate a parameter using a parent index/name
- CreateParameter
(pdId, value): create a new parameter value for the given definition ID
Info
For more, see the BaseModule cover page and linked method references.
Common patterns¶
-
Normalize + validate shape
- Trim, collapse whitespace
- Enforce regex pattern(s)
- Reformat into canonical representation
-
Cross‑field checks
- Compare a numeric total against line‑item sum
- Ensure Country (Rule Type) and Address country agree
-
Dataset validation
- Enforce “value in allowed list” via Custom Dataset lookup
-
External verification (lightweight)
- Validate a code/ID via an API; add verification note/status on pass/fail
- Respect Code Execution Timeout; handle timeouts gracefully
-
Confidence and reviewer guidance
- Adjust confidence conservatively
- Add meaningful verification notes for reviewers (“Expected ABC‑1234 pattern”)
Examples¶
Example 1 — Normalize and verify a code with regex¶
// Imports (add in Imports tab): System.Text.RegularExpressions
// Goal: Ensure value is ABC-1234 shape; add verification status and normalize.
if (verification == null || string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(verification.Value))
{
// Keep as-is; allow other rules to decide on HITL if required
return verification;
}
// Trim + collapse spaces
var raw = Regex.Replace(verification.Value.Trim(), @"\s+", " ");
// Try to coerce "ABC_ 1234" → "ABC-1234"
var m = Regex.Match(raw, @"^([A-Za-z]{3})\s*[-_ ]?\s*(\d{4})$");
if (m.Success)
{
var canonical = $"{m.Groups[1].Value.ToUpperInvariant()}-{m.Groups[2].Value}";
verification.Value = canonical;
// Mark as verified by script
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Scripted | VerificationStatus.Verified, canonical, "Normalized by Script");
}
else
{
// Flag as suspicious for HITL routing by downstream workflow
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Susicious, raw, "Pattern mismatch: expected ABC-1234");
}
return verification;
Example 2 — Cross-check against a Custom Dataset¶
// Use a dataset to validate that the value is in an allowed list.
// Assumes you know the dataset definition ID and field ID to match against.
const int dataSetDefId = /* your dataset def ID */;
const int allowedFieldId = /* your field ID inside the dataset */;
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(verification?.Value))
{
var ds = module.GetDataSetByDef(stpd, dataSetDefId, false, false, null, null, null, null);
var field = ds?.FindField(allowedFieldId);
if (ds != null && field != null)
{
var matches = module.GetDataSetRecords(ds, field, verification.Value.Trim(), /*isExactMatch*/ true);
if (matches == null || !matches.Any())
{
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Susicious, verification.Value, "Value not in allowed dataset");
}
else
{
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Scripted | VerificationStatus.Verified, verification.Value, "Validated against dataset");
}
}
}
return verification;
Example 3 — Call an external API with timeout¶
// Assemblies: System.Net.Http
// Imports: System.Net.Http, System.Text.Json
using var http = new HttpClient { Timeout = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10) };
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(verification?.Value))
return verification;
var payload = new { value = verification.Value };
var content = new StringContent(System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Serialize(payload), System.Text.Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
try
{
var resp = await http.PostAsync("https://api.example.com/validate", content);
if (resp.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var json = await resp.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
// parse response, update value or confidence accordingly
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Scripted, verification.Value, "Validated via external API");
}
else
{
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Susicious, verification.Value, $"API error: {resp.StatusCode}");
}
}
catch (TaskCanceledException)
{
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Susicious, verification.Value, "API timeout");
}
return verification;
HITL and verification guidance¶
Escalate to review (via Workflow Script or your routing policy) when:
- Pattern/shape validation fails or is ambiguous
- Dataset/API validations don’t confirm the value
- Confidence drops below your minimum acceptable threshold
- Cross‑field rules conflict (e.g., totals mismatch)
Suggested reviewer notes (HITL)
- “Check format: expected ABC‑1234; confirm hyphen placement.”
- “Value not found in Allowed Dataset v2025‑08; pick from list or correct OCR.”
- “API validation timed out; re‑try or confirm from source document.”
Best practices¶
- Keep field scripts focused; do heavy orchestration at service-level utilities or Workflow Script.
- Fail safe: when unsure, add a clear verification note and let routing handle HITL.
- Use Imports/Assemblies sparingly; include only what you need.
- Respect timeouts; avoid long-running or synchronous loops.
- Log the why: verification notes should explain the decision in one sentence.
- Version regularly; use History to compare and restore known-good versions.
Testing checklist¶
- Happy paths: valid inputs normalize and verify as expected
- Negative paths: invalid inputs add Suspicious status and clear reviewer guidance
- Timeouts/API failures: handled safely; do not block pipeline
- Dataset validations: exact vs. fuzzy lookups behave per policy
- Performance: completes within configured timeout
- Return contract: always returns ProcessResult(verification)
Troubleshooting¶
- Compilation errors
- Check the Compilation Results pane; add required Imports/Assemblies; correct syntax
- Script made no change
- Ensure you assign verification.Value and return ProcessResult(verification)
- Verification notes not visible
- Use module.AddVerification(…) and verify your viewer shows verification history
- “Not all code paths return a value”
- Ensure every branch ends by returning ProcessResult(verification)
- External calls failing
- Confirm assembly references, network policies, and timeouts; add exception handling
See also¶
- Custom Code overview and samples: Custom Code
- Base APIs and data types: BaseModule / IBaseModule
UI reference¶
- Code Editor
- Imports
- Assemblies
- History (Compare/Restore)