Workflow Script (Field Enhancement)¶
Use the Workflow Script enhancement to drive routing, HITL (Human‑in‑the‑Loop) assignments, escalations, and cross‑service orchestration based on a field’s value and context. It complements Script by focusing on workflow actions: creating work items, copying/moving documents, setting statuses, and enforcing verification policies.
When to use¶
- Create or assign Work Items for manual review when values are out of policy.
- Escalate to admin/supervisors under specific conditions (e.g., low confidence, overdue).
- Copy or move documents to other services based on business rules.
- Set verification statuses/flags and provide reviewer guidance automatically.
Open Field Configuration¶
See Field Rules (Rules Engine) for how to open the field configuration:
- From the document overlay (supported services), or
- From the Fields panel on the right sidebar.
Configure the Workflow Script enhancement¶
The Workflow Script panel mirrors the Script UI with four tabs:
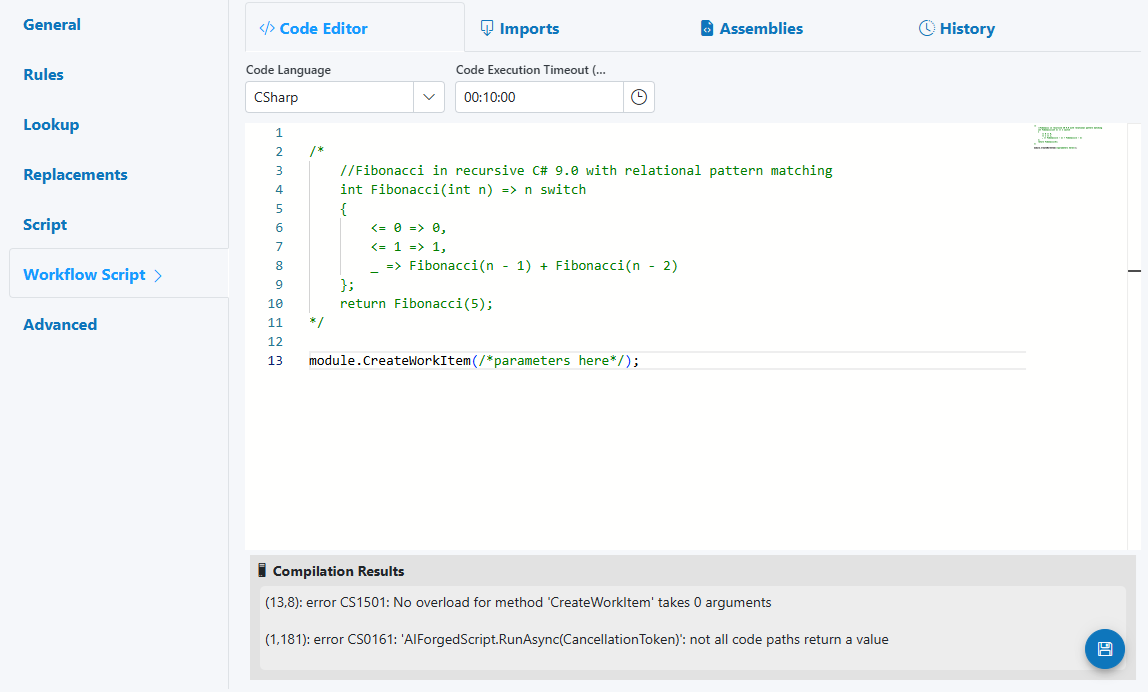
-
Code Editor
- Code Language (C#, IronPython; SemanticKernel if enabled)
- Code Execution Timeout
- Compilation Results pane (errors, warnings)
-
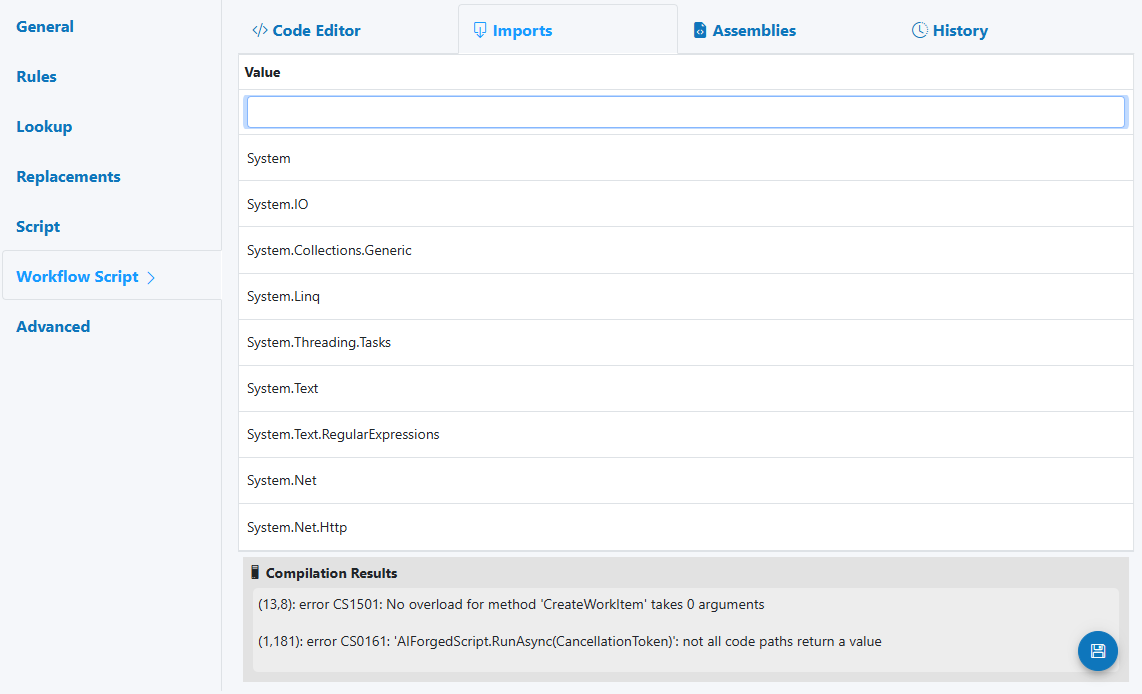
Imports
- Add namespaces (e.g., System.Text.RegularExpressions, System.Net.Http)
-
Assemblies
- Reference .NET assemblies your script requires
-
History
- Versioned changes with Compare and Restore
Execution model and return contract¶
- Scope: Runs for the specific field (Parameter Definition) it is attached to.
- Order (typical Field Enhancements pipeline): Replacements → Lookup → Script → Verification Services → Workflow Script → Advanced
- Input: verification (current field value and context), plus document/project context via module
- Output: Return a ProcessResult using the current verification
Example return (do not code fence this in your editor): return verification;
Workflow focus
Use Script for value transformations and validation. Use Workflow Script for actions—creating work items, moving/copying documents, and orchestrating verification flow.
Supported languages¶
- C#
- IronPython
- SemanticKernel (Natural language coding, if enabled)
Tip
Prefer C# for the richest API and samples; IronPython suits Python‑centric teams. SemanticKernel can speed up “policy-in-plain‑English” logic and prototypes.
What’s available (BaseModule overview for workflow)¶
All BaseModule APIs are available (same as Script), with emphasis on HITL and orchestration:
- Work Items (HITL)
- Create, assign, prioritize, and escalate work items.
- KPI‑informed assignment helpers (e.g., pick random, idle, or high‑throughput users).
- Documents and Services
- Copy/Move documents to other services; update status and comments.
- Parameters and Verifications
- Read/modify verification state; add reviewer guidance; set flags for routing.
- Datasets, Webhooks, Notifications
- Lookup or persist context; call webhooks for external systems.
See: - Base module and types: BaseModule / IBaseModule - Custom Code reference: Custom Code
Security
Only use approved endpoints/assemblies; keep secrets in secure configuration, not in code.
Reference: field‑level context (globals)¶
Available objects in field‑level Workflow Script:
- module: TModule (IBaseModule) — your entry point to AIForged APIs
- project: IProject — current project
- stpd / def: IParameterDef — current field definition
- stl: int — language context/index (if applicable)
- rule: BaseOption — active rule option (if relevant)
- logger: ILogger — write audit/debug logs
Current document/field:
- doc: IDocument — current document
- par: IDocumentParameter — current parameter instance
- verification: IVerification — current field verification
- step: VerificationStep — verification step
IVerificationModule adds convenient helpers:
- FindParameter(pdId, includeVerification = false, index = null)
- FindParameterByParentIndex(pdId, parentName, includeVerification = false)
- CreateParameter
(pdId, value)
Info
For more, see BaseModule.
Common workflow patterns¶
- Create a Work Item for HITL when a field fails validation.
- Assign tasks based on availability or KPIs (random, idle, high‑throughput).
- Escalate to Admin if SLAs are breached or confidence drops below threshold.
- Copy/Move document to a specialized service for follow‑up processing.
- Set DocumentStatus and add comments for audit and downstream automation.
- Add verification entries with reviewer guidance to speed decisions.
Examples¶
Example 1 — Create a Work Item for verification¶
// If confidence is low or a policy fails, create a HITL task
if (verification == null || verification.Confidence < 0.75)
{
// pick a verifier (implement your own selection or use helpers)
var users = module.GetUsers(project.Id, null, null, null); // filter as needed
var chosen = module.PickRandom(users?.Select(u => u.user).Distinct().ToList(), null);
if (chosen != null)
{
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Required, verification?.Value, "Routed to HITL");
module.CreateWorkItem(
chosen.UserId,
WorkItemType.Document,
WorkItemStatus.Created,
WorkItemAction.Verify,
WorkItemMethod.Random,
TimeSpan.FromHours(24),
stpd.Id, // serviceId or parent service id if needed
doc.Id,
null, null, null, null, null,
"Verify field value; low confidence",
$"Field {stpd.Name} needs review: {verification?.Value}"
);
module.SaveChanges();
}
}
return verification;
Example 2 — Escalate overdue items to Admin¶
// If previous verification indicates overdue or repeated failure, escalate
bool overdue = /* your SLA logic here */;
if (overdue)
{
var admins = module.GetUsers(stpd.Id, null, [GroupRoleType.Administrator], null);
var admin = admins?.Select(x => x.user).FirstOrDefault();
if (admin != null)
{
module.AddVerification(verification, VerificationStatus.Susicious, verification?.Value, "Escalated due to SLA breach");
module.CreateWorkItem(
admin.UserId,
WorkItemType.Document,
WorkItemStatus.Escalated,
WorkItemAction.Review,
WorkItemMethod.Manual,
TimeSpan.FromHours(12),
stpd.Id,
doc.Id,
null, null, null, null, null,
"Escalation: SLA breached",
$"Field {stpd.Name} requires supervisor attention"
);
module.SaveChanges();
}
}
return verification;
Example 3 — Copy or Move the document to another service¶
// Route document to a follow-up service after policy check
bool needsFollowUp = /* your policy */;
if (needsFollowUp)
{
int targetServiceDefId = /* destination service def id */;
module.CopyDocument(doc, targetServiceDefId, DocumentStatus.Queued, UsageType.Inbox, null, null);
module.SetDocumentStatus(doc, DocumentStatus.InterimProcessed, "Routed to follow-up service", "Copied for further processing", true, true, true);
module.SaveChanges();
}
return verification;
Example 4 — Assign using idle-user fallback¶
// Try KPI-based chooser; if none, fallback to idle user
string userId = module.GetHighThroughputUserId(DateTime.Now.AddDays(-7), DateTime.Now, null, WorkItemType.Document, WorkItemAction.Verify, WorkItemStatus.Created);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(userId))
{
userId = module.GetIdleUserId(WorkItemType.Document, WorkItemAction.Verify, DateTime.Now.AddDays(-30), DateTime.Now, null);
}
// Create work item for selected user
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(userId))
{
module.CreateWorkItem(userId, WorkItemType.Document, WorkItemStatus.Created, WorkItemAction.Verify, WorkItemMethod.Manual, TimeSpan.FromHours(24), stpd.Id, doc.Id, null, null, null, null, null, "Verify via idle/high-throughput selection", null);
module.SaveChanges();
}
return verification;
HITL triggers and reviewer guidance¶
Trigger Work Items or escalate when:
- Field confidence is below your threshold, or rules/lookup validation fails.
- Ambiguous values or cross‑field inconsistencies occur (totals, dates, IDs).
- SLA or age conditions require re‑assignment or supervisor review.
Suggested reviewer notes (HITL)
- “Confirm format and value; see policy note in the comment.”
- “Cross‑field mismatch detected; verify total vs line‑item sum.”
- “Escalation due to overdue verification; prioritize completion.”
Best practices¶
- Keep Workflow Script action‑oriented: create/assign/escalate; avoid heavy transformations here.
- Commit often: call SaveChanges() after creating work items or status changes.
- Use structured, concise messages for work items and verification notes.
- Centralize user selection logic (KPI, idle, random) to keep behavior consistent.
- Log decisions (who, why, when) to streamline audits and tuning.
Deterministic routing
Combine KPI selection with a stable fallback (idle → random) to avoid unassigned tasks when data is sparse.
Testing checklist¶
- Happy paths: create a Work Item on intended conditions.
- Negative paths: no work item when conditions are not met.
- KPI/idle/random selection: verify correct user resolution and fallbacks.
- Copy/Move routing: confirm documents arrive at the target service with correct status.
- Performance: scripts complete within the configured timeout.
- Return contract: always returns ProcessResult(verification).
Troubleshooting¶
-
Compilation errors (e.g., CS1501: wrong overload)
- Check method signatures; required parameters must be provided.
- Review the Compilation Results pane for precise line/column errors.
-
“Not all code paths return a value”
- Ensure every branch ends with return verification;
-
Work Items not appearing
- Confirm user selection returns a valid user ID.
- Call SaveChanges() after CreateWorkItem.
-
Routing didn’t occur
- Verify target service definition IDs and document statuses.
- Check logs for conditional logic skipping execution.
Security
Do not hard‑code secrets or PII in scripts. Use secure settings and approved endpoints only.
See also¶
- Base APIs and data types: BaseModule / IBaseModule
- Custom Code utility (service‑level orchestration): Custom Code
- Work Items and HITL concepts: see your team’s internal SOPs and queues setup
UI reference¶
- Code Editor

- Imports
- Assemblies
- History (Compare/Restore)