Number¶
Use the Number Rule Type when a field should contain a numeric value. The rule validates and normalizes the extracted number, applies culture-aware formatting, and can accept multiple input styles while producing a single, consistent output.
When to use¶
- Quantities, unit prices, totals that are not currencies, rates, percentages (as raw numbers), counts, IDs composed strictly of digits.
- Any field that must be parsed as a number with consistent decimal and thousands separators.
Open Field Configuration¶
See Field Rules (Rules Engine) for how to open the field configuration:
- From the document overlay (supported services), or
- From the Fields panel on the right sidebar.
Configure the Number rule¶
Core settings:
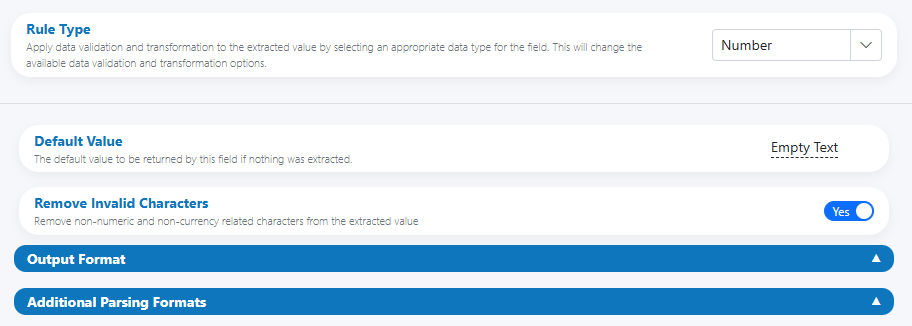
- Rule Type: Number
- Default Value: The value to return when nothing is extracted (e.g., Empty Text or 0).
- Remove Invalid Characters: Removes non‑numeric and non‑number‑related characters (e.g., stray letters or labels) before parsing.
Keep it clean
Enable “Remove Invalid Characters” to strip labels like “Qty:” or stray spaces before parsing. Signs (+/−), decimal, and group separators that match your configuration are preserved.
Input parsing and normalization¶
Use “Additional Parsing Formats” to accept multiple input cultures while converging to one output style.
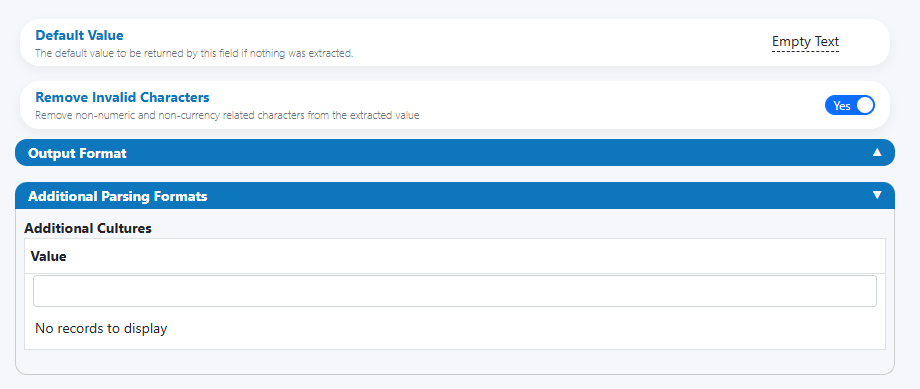
- Additional Cultures (optional)
- Add culture codes you want to accept during parsing (e.g.,
en-US,de-DE,fr-FR). This helps interpret comma vs dot usage correctly.
- Add culture codes you want to accept during parsing (e.g.,
- Normalization behavior
- The parser interprets the input according to the allowed cultures, then converts to your chosen output format (see next section).
Separator ambiguity
Different sources may use “,” as decimal and “.” as thousands (e.g., 1.234,56). Add the relevant input culture(s) so the parser chooses the right meaning consistently.
Output and formatting¶
Define the culture and presentation of the final output in the Output Format panel.
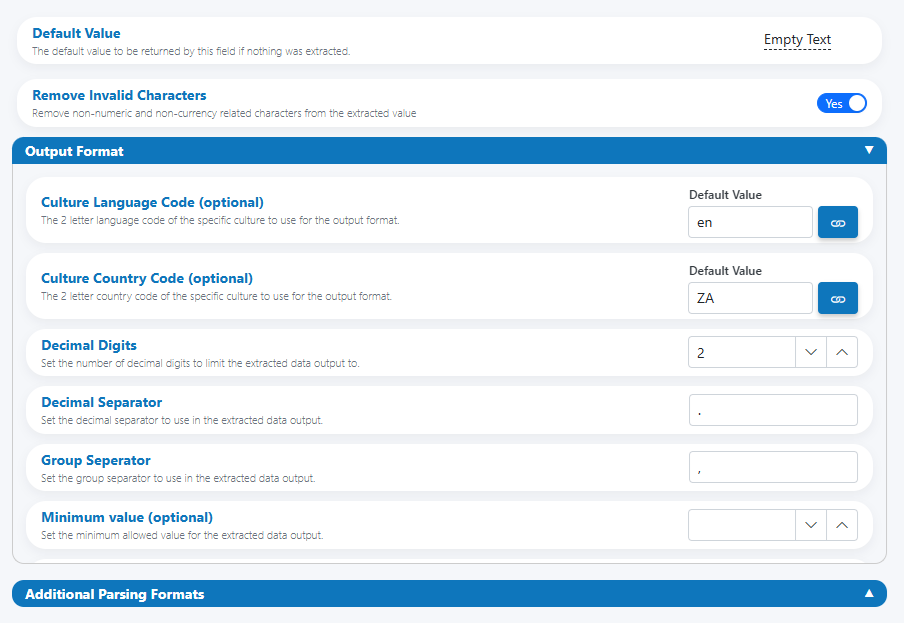
- Culture Language Code (optional): e.g.,
en,fr - Culture Country Code (optional): e.g.,
US,ZA - Decimal Digits: number of fraction digits to output (e.g., 0, 2, 4)
- Decimal Separator: character for decimals (e.g.,
.or,) - Group Separator: character for thousands (e.g.,
,,) - Minimum value (optional): set a lower bound for acceptable values
Culture vs explicit separators
Culture provides sensible defaults for separators and grouping. If you set Decimal/Group Separators explicitly, those override culture defaults.
HITL triggers and reviewer guidance¶
Trigger review when:
- The value cannot be parsed under any configured culture.
- The parsed value is outside policy (e.g., below Minimum or otherwise not expected to be negative/zero).
- Fraction digits exceed the configured Decimal Digits limit (if strict).
- Input appears ambiguous (e.g., both
.and,present in unexpected positions).
Suggested reviewer note (HITL)
“Verify the numeric value and separators. If thousands/decimal separators look incorrect, correct them and ensure the final value matches the expected precision (Decimal Digits).”
Examples¶
-
Standardize mixed separators
- Inputs:
1,234.5,1.234,5(EU style) - Additional Cultures:
en-US,de-DE - Output Format: Language
en, CountryZA, Decimal.Group,, Decimal Digits2 - Result:
1,234.50
- Inputs:
-
Integer-only field
- Decimal Digits:
0 - Input:
2 345→ Output:2,345
- Decimal Digits:
-
Reject out-of-policy values
- Minimum value:
0 - Input:
-12.5→ Escalate (negative not allowed)
- Minimum value:
Quantities vs money
Use Number for non-monetary values (quantities, rates). Use Currency for monetary amounts where currency symbols and currency-specific formatting matter.
Best practices¶
- “Parse wide, format narrow”: accept the realistic input cultures you see; output a single, consistent style.
- Set Decimal Digits explicitly to control precision and rounding for downstream systems.
- If negatives are not allowed, enforce with Minimum value and HITL on violations.
- Keep Group Separator consistent across your system to avoid confusion in exports and CSVs.
Testing checklist¶
- [ ] Inputs using
.vs,as decimal separators (and the opposite for thousands). - [ ] Values with varying precision (e.g., 0, 2, 4 decimals) against your Decimal Digits setting.
- [ ] Large numbers with grouping and without grouping.
- [ ] Edge cases: zero, negative values (if allowed), and scientific notation (if expected).
- [ ] Confirm Additional Cultures cover all sources.
- [ ] Verify Minimum value behavior and associated HITL trigger.
Troubleshooting¶
-
Parses incorrectly (wrong decimal/grouping)
- Add/adjust Additional Cultures to match the source; verify explicit Decimal/Group Separator overrides.
-
Value won’t parse
- Ensure “Remove Invalid Characters” is enabled; check for hidden characters; confirm the input’s culture is included.
-
Unexpected rounding
- Review Decimal Digits; if stricter control is needed, escalate when fraction digits exceed the configured precision.
-
Negative value blocked
- Check Minimum value and policy; allow negatives only where the business logic permits.
UI reference¶
-
Base panel (Rule Type, Default Value, Remove Invalid Characters)

-
Output Format (culture, separators, precision, minimum)

-
Additional Parsing Formats (cultures)
